to what do the cam, c3 and c4 pathways refer?

The assimilation of carbon dioxide from the sunlight, for the procedure of photosynthesis and so converting it to glucose (energy) synthesizing different product is the fundamental departure betwixt the three. So during the CO2 fixation, when the photosynthetic plants produce 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) or 3- carbon acid as the first product is called C3 pathway.
But when the photosynthetic plant, prior going to the C3 pathway, produces oxaloacetic acrid (OAA) or 4 -carbon compound as their first stable product is called equally C4 or Hatch and Slack pathway. But when the plants absorb the energy of the sunlight at the twenty-four hours time and utilize this energy for the assimilation or fixing the carbon dioxide at night time is called as crassulacean acid metabolism or CAM.
These procedures are followed past plants, certain species of bacteria and algae for the production of free energy, independent of their habitat. The synthesis of energy, using carbon dioxide and water as the primary source to gain nutrients from air and h2o is termed as photosynthesis. This is the prime number process for the living being which produces food on their own
In this content, we will be considering the essential difference between the three types of pathways followed by plants and few microorganisms and a pocket-sized clarification about them.
Content: C3, C4, and CAM pathways
- Comparison Chart
- Definition
- Fundamental Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Ground for Comparison | C3 pathway | C4 pathway | CAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Such plants whose get-go product after the carbon assimilation from sunlight is 3-carbon molecule or 3-phosphoglyceric acid for the production of free energy is called C3 plants, and the pathway is called as the C3 pathway. It is near commonly used past plants. | Plants in the tropical area, convert the sunlight free energy into C4 carbon molecule or oxaloacetice acid, which takes place earlier the C3 wheel and then it further convert into the energy, is called C4 plants and pathway is called as the C4 pathway. This is more efficient than the C3 pathway. | The plants which store the energy from the sun and then catechumen it into free energy during nighttime follows the CAM or crassulacean acid metabolism. |
| Cells involved | Mesophyll cells. | Mesophyll prison cell, bundle sheath cells. | Both C3 and C4 in aforementioned mesophyll cells. |
| Instance | Sunflower, Spinach, Beans, Rice, Cotton. | Sugarcane, Sorghum and Maize. | Cacti, orchids. |
| Can be seen in | All photosynthetic plants. | In tropical plants | Semi-arid status. |
| Types of plants using this bike | Mesophytic, hydrophytic, xerophytic. | Mesophytic. | Xerophytic. |
| Photorespiration | Present in high rate. | Not easily detectable. | Detectable in the afternoon. |
| For the product of glucose | 12 NADPH and eighteen ATPs are required. | 12 NADPH and 30 ATPs are required. | 12 NADPH and 39 ATPs are required. |
| Showtime stable product | 3-phosphoglycerate (iii-PGA). | Oxaloacetate (OAA). | Oxaloacetate (OAA) at nighttime, iii PGA at daytime. |
| Calvin cycle operative | Alone. | Along with the Hatch and Slack cycle. | C3 and Hatch and Slack bicycle. |
| Optimum temperature for photosynthesis | fifteen-25 °C | thirty-twoscore °C | > forty degrees °C |
| Carboxylating Enzyme | RuBP carboxylase. | In mesophyll: PEP carboxylase. In package sheath: RuBP carboxylase. | In the dark: PEP carboxylase. In lite: RUBP carboxylase. |
| CO2: ATP: NADPH2 ratio | 1:three:2 | 1:5:ii | ane:6.five:ii |
| Initial CO2 acceptor | Ribulose-1,5-biphophate(RuBP). | Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). | Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). |
| Kranz Anatomy | Absent. | Nowadays. | Absent. |
| CO2 compensation point (ppm) | 30-70. | six-10. | 0-five in dark. |
Definition of a C3 pathway or Calvin wheel.
C3 plants are known as cool-season or temperate plants. They grow best at an optimum temperature between 65 to 75°F with the soil temperature suited at 40- 45°F. These types of plants testify less efficiency at high temperature.
The chief product of C3 plants is three-carbon acid or 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA). This is considered as the first product during carbon dioxide fixation. The C3 pathway completes in three steps: carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration.
C3 plants reduce into the CO2 directly in the chloroplast. With the help of ribulose biphosphate carboxylase (RuBPcase), the two molecules of 3-carbon acid or 3-phosphoglyceric acid are produced. This 3- phosphoglyceric justifies the name of the pathway as C3.
In some other step, NADPH and ATP phosphorylate to requite iii-PGA and glucose. And and so the wheel again starts by regenerating the RuBP.
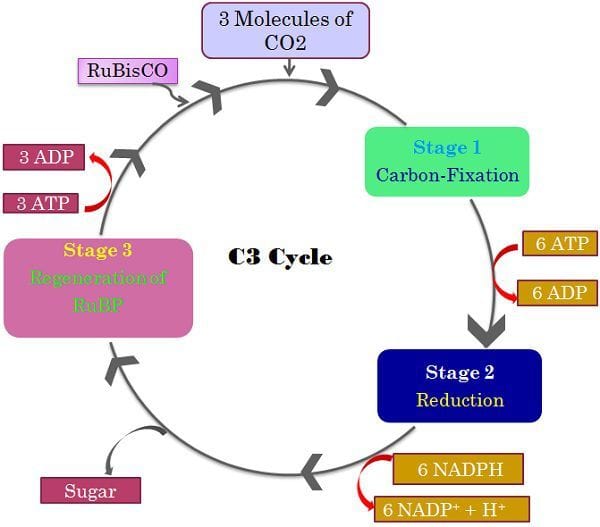
The C3 pathway is the single step process, takes place in the chloroplast. This organelle deed every bit the storage of sunlight energy. Of the full establish present on earth, 85 percent uses this pathway for the production of energy.
The C3 plants can be perennial or almanac. They are highly proteinaceous than the C4 plants. The examples of annual C3 plants are wheat, oats, and rye and the perennia50 plants include fescues, ryegrass, and orchardgrass. C3 plants provide a higher amount of poly peptide than the C4 plants.
Definition of C4 pathway or Hatch and Slack pathway.
Plants, especially in the tropical region, follow this pathway. Before Calvin or C3 bike, some plants follow the C4 or Hatch and Slack pathway. It is a two stride procedure where Oxaloacetic acid (OAA) which is a 4-carbon chemical compound is produced. It occurs in mesophyll and packet sheath jail cell present in a chloroplast.
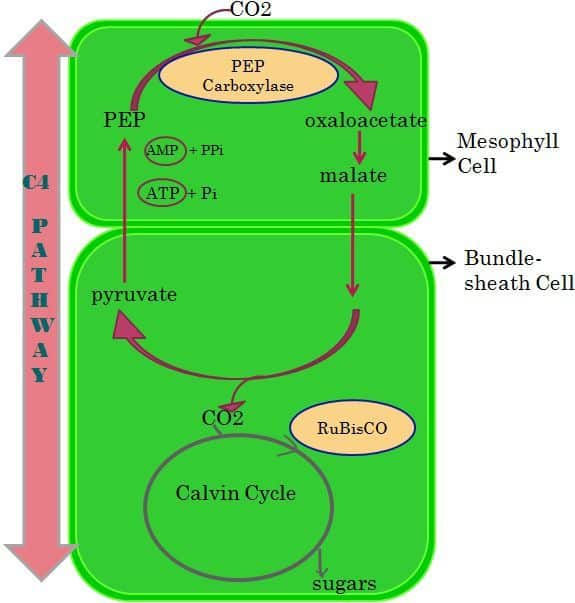
When the four-carbon compound is produced, it is sent to the bundle sheath jail cell, hither the 4-carbon molecule farther get splits into a carbon dioxide and the 3-cabon compound. Somewhen, the C3 pathway starts to produce energy, where the iii-carbon compound act as the precursor.
C4 plants are also known every bit warm-flavor or tropical plants. These can exist perennial or annual.The perfect temperature to grow for these plants is 90-95°F. The C4 plants are much more efficient in utilizing nitrogen and gathering carbon dioxide from the soil and atmosphere. The protein content is low as compared to C3 plants.
These plants got their name from the product called equally oxaloacetate which is four carbon acid. The examples of perennial C4 plants are Indian grass, Bermudagrass, switchgrass, large bluestem and that of annual C4 plants are sudangrasses, corn, pearl millet.
Definition of CAM plants
The noteworthy remark which distinguishes this process from the above two is that in this blazon of photosynthesis the organism absorbs the energy from the sunlight at the day fourth dimension and uses this free energy at the night time for the assimilation of carbon dioxide.
Information technology is a kind of accommodation at the fourth dimension of periodic drought. This process permits an exchange of gases at the night fourth dimension when the air temperature is cooler, and there is the loss of h2o vapor.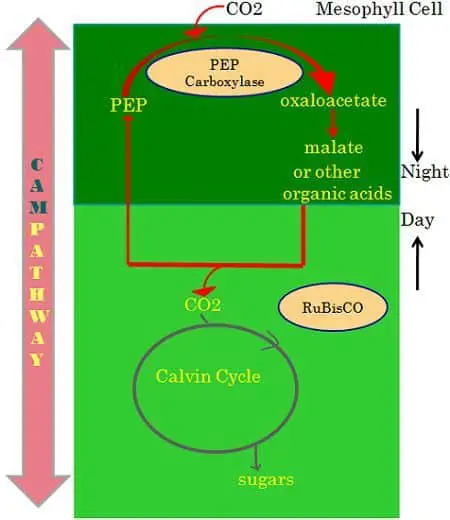
Around 10% of the vascular plants accept adapted the CAM photosynthesis only mainly found in plants grown in the arid region. The plants like cactus and euphorbias are the examples. Fifty-fifty the orchids and bromeliads, adapted this pathway due to an irregular water supply.
In the 24-hour interval time, malate gets decarboxylated to provide CO2 for the fixation of the Benson-Calvin wheel in closed stomata. The primary characteristic of CAM plants is an assimilation of CO2 at night into malic acid, stored in the vacuole. PEP carboxylase plays the main function in the product of malate.
Cardinal Differences of C3, C4 and CAM plants.
Above nosotros discuss the process for obtaining the free energy of these dissimilar types, below we will discuss the key differences among iii:
- C3 pathway or C3 plants can be defined every bit those kind plants whose first product after the carbon assimilation from sunlight is 3-carbon molecule or 3-phosphoglyceric acid for the product of energy. It is most commonly used past plants; While plants in tropical area, convert the sunlight free energy into C4 carbon molecule or oxaloacetic acid, this wheel takes place earlier the C3 bike and then with the aid of enzymes it carries the further process of getting nutrients, is called C4 plants and pathway is called as C4 pathway. This pathway is more efficient than the C3 pathway. On the other paw, the plants which store the energy from the sun at day time and so convert it into energy at night follows the CAM or crassulacean acid metabolism.
- Cells involved in a C3 pathway are mesophyll cells and to that of the C4 pathway are mesophyll cell, packet sheath cells, just CAM follows both C3 and C4 in same mesophyll cells.
- An instance of C3 are Sunflower, Spinach, Beans, Rice, Cotton, while the example of C4 plants is Sugarcane, Sorghum, and Maize, and Cacti, orchids are the instance of CAM plants.
- C3 tin can be seen in all photosynthetic plants, while C4 is followed by tropical plants and CAM past Semi-barren condition plants.
- Types of plants using C3 cycle are mesophytic, hydrophytic, xerophytic but C4 is followed in mesophytic plants and Xerophytic follows CAM.
- Photorespiration is nowadays in the college charge per unit while information technology is non easily detectable in C4 and CAM.
- 12 NADPH and 18 ATPs in the C3 cycle; 12 NADPH and 30 ATPs in C4 and 12 NADPH and 39 ATPs are required for the production of glucose.
- 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) is first stable production of C3 pathway; Oxaloacetate (OAA) for C4 pathway and Oxaloacetate (OAA) at night, 3 PGA at daytime in CAM.
- Optimum temperature for photosynthesis in C3 is xv-25 ° C; 30-40 ° C in C4 plants and > 40°C in CAM
- Carboxylating Enzyme is RuBP carboxylase in C3 plants, but in C4 plants it is PEP carboxylase (in mesophyll) and RuBP carboxylase (in bundle sheath) while in CAM it is PEP carboxylase (in the night) and RuBP carboxylase (in lite).
- CO2: ATP: NADPH2 ratio 1:3:2 in C3, 1:5:2 in C4 and ane:6.five:2 in CAM.
- The initial CO2 acceptor is Ribulose-one,v-biphophate(RuBP) in a C3 pathway and Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in C4 and CAM.
- Kranz Anatomy is nowadays in the C4 pathway merely, and it is absent in C3 and CAM plants.
- The CO2 compensation point (ppm) is 30-70 in C3 establish; 6-10 in C4 plants and 0-5 in the dark in CAM.
Conclusion
We all are aware of the fact that plants prepare their food, past the process of photosynthesis. They catechumen atmospheric carbon dioxide into plant food or energy (glucose). But as the plants grow in the different habitat, they have different atmospheric and climatic status; they differ in the procedure of gaining energy.
Like in case C4 and CAM pathways are the 2 adaptations arose past natural selection, for the survival of the plants of high temperature and arid region. So nosotros tin can say that these are the three distinct biochemical methods, of plants to obtain energy and C3 is the almost mutual among them.
Source: https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-c3-c4-and-cam-pathway.html